Kalibraatio: The Backbone of Precision in Modern Technology
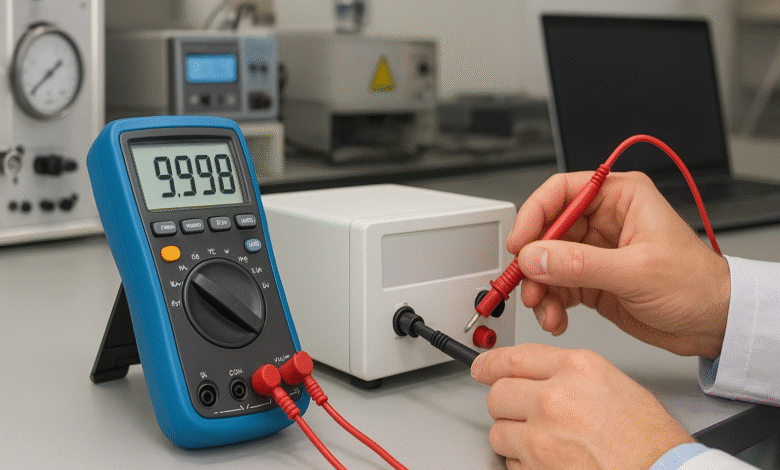
Introduction to Kalibraatio
The term kalibraatio, which is Finnish for calibration, may sound like something only scientists or engineers deal with. However, it plays a vital role in nearly every aspect of modern technology. From ensuring your smartphone’s sensors work correctly to guaranteeing the accuracy of hospital ventilators and aircraft instruments, kalibraatio is the hidden force that ensures devices perform as expected.
The Origins of Kalibraatio
Although often seen as a product of modern engineering, kalibraatio has existed for thousands of years. Early civilizations used standardized weights to measure goods during trade, laying the foundation for today’s calibration practices. As technology evolved, calibration transformed into a structured scientific discipline, becoming indispensable in industries where accuracy could mean the difference between success and disaster.
Why Kalibraatio Is More Crucial Than Ever
In our data-driven world, even a small measurement error can lead to severe consequences. A miscalibrated medical device could result in an incorrect diagnosis, while uncalibrated aviation instruments could endanger lives. This shows why kalibraatio is more important than ever in ensuring accuracy, reliability, and safety across industries.
The Science Behind Kalibraatio
At its core, kalibraatio involves comparing the output of an instrument with a recognized standard. These standards, maintained by organizations such as the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), guarantee consistency worldwide.
-
Tolerance and Accuracy: Every instrument has an acceptable margin of error, called tolerance. Calibration ensures measurements remain within this range, maintaining accuracy.
-
Traceability: Proper calibration guarantees that every measurement can be traced back to a national or international standard, making the results universally valid.
Types of Kalibraatio
Different instruments require different calibration methods. Some major types include:
-
Electrical Calibration – Ensures accuracy in devices like voltage meters and oscilloscopes.
-
Mechanical Calibration – Covers torque, pressure, and force gauges. An uncalibrated pressure gauge in an industrial boiler could be extremely dangerous.
-
Thermal and Optical Calibration – Critical for temperature sensors, light meters, and laboratory equipment.
-
Chemical and Laboratory Calibration – Used for pH meters, balances, and spectrophotometers to maintain laboratory accuracy.
Industries Relying on Kalibraatio
-
Healthcare: Devices like infusion pumps and MRI scanners depend on precise calibration for patient safety.
-
Aerospace and Aviation: Instruments such as altitude sensors and GPS systems require flawless accuracy.
-
Automotive and Manufacturing: Robots and safety systems rely on regular calibration to maintain efficiency.
-
Telecommunications: Network testing tools and analyzers must be calibrated for consistent connectivity.
The Calibration Process
The process of kalibraatio involves several steps:
-
Inspection – Instruments are checked for damage before calibration begins.
-
Calibration Procedure – Measurements are compared with standards, and adjustments are made if necessary.
-
Certification – A calibration certificate is issued, confirming compliance with industry standards.
Tools Used in Kalibraatio
-
Calibrators and Standards: High-precision tools that act as benchmarks.
-
Sensors and Meters: Used to measure variables such as temperature and pressure.
-
Calibration Software: Assists in data recording, analysis, and even automated adjustments.
Scheduling and Frequency of Kalibraatio
-
When to Calibrate: Frequency depends on usage, environment, and manufacturer recommendations. High-risk industries require more frequent calibration.
-
Risks of Skipping Calibration: Inaccurate readings, equipment failure, legal issues, and safety hazards.
-
Calibration Planning: Many companies use software or service partners to maintain a consistent schedule.
Regulatory Role in Kalibraatio
-
ISO/IEC 17025: Recognized globally as the standard for calibration laboratories.
-
Industry-Specific Regulations: Organizations like the FDA (healthcare) and FAA (aviation) mandate strict calibration requirements.
-
Compliance: Regular audits and certified labs ensure that calibration meets regulatory standards.
Digital Transformation in Kalibraatio
Technology has modernized calibration practices significantly.
-
IoT and Smart Devices: Equipment now alerts users when calibration is needed.
-
Remote and Automated Calibration: Especially useful in industries such as oil and gas.
-
Cloud-Based Management: Provides centralized calibration record storage for better compliance and efficiency.
Benefits of Proper Kalibraatio
-
Accuracy and Reliability: Ensures trusted data and consistent results.
-
Safety and Compliance: Prevents workplace accidents and legal risks.
-
Cost Savings: Reduces downtime, waste, and equipment wear, improving overall efficiency.
Challenges in Kalibraatio
Despite its benefits, calibration faces challenges:
-
Environmental Factors: Temperature, humidity, and vibration can impact results.
-
Human Error: Even advanced equipment is vulnerable if misused.
-
Technological Limits: Some instruments may not support the required precision.
Common Myths About Kalibraatio
-
“It’s only for advanced industries.” → False. Even a coffee machine requires calibration for consistent taste.
-
“Calibration once is enough.” → Incorrect. Instruments naturally drift over time.
-
“It’s too expensive.” → In reality, the cost of not calibrating is far higher due to failures and downtime.
The Future of Kalibraatio
Emerging technologies are shaping the future of calibration:
-
AI and Machine Learning: Used to optimize calibration intervals and predict instrument drift.
-
Predictive Maintenance: Helps anticipate when calibration is needed, saving time and money.
-
Blockchain: Provides secure and immutable calibration record-keeping.
Conclusion
In conclusion, kalibraatio is not just a technical requirement but the foundation of precision in modern technology. Whether in healthcare, aviation, or manufacturing, it ensures safety, reliability, and efficiency. The next time you use a device that gives you an accurate reading—whether it’s your smartphone’s GPS or a medical thermometer—remember that kalibraatio is working quietly behind the scenes.
FAQs about Kalibraatio
Q1: What does kalibraatio mean?
Kalibraatio is the Finnish term for calibration, which refers to adjusting and verifying instruments to ensure accurate measurements.
Q2: How often should calibration be performed?
The frequency depends on usage, environment, and industry standards. High-risk industries require more frequent calibration.
Q3: Why is calibration important in healthcare?
Medical devices like ventilators, infusion pumps, and MRI scanners must be calibrated to avoid life-threatening errors.
Q4: What are the risks of ignoring calibration?
Skipping calibration can lead to inaccurate data, equipment failures, safety hazards, and regulatory penalties.
Q5: What is the future of kalibraatio?
The future lies in AI-driven predictive calibration, IoT-based self-monitoring, and blockchain-secured calibration records.
Read also:Lopalapc2547 New Version Released: Complete Guide and Features



